The discovery by the Israel Antiquities Authority in Jerusalem’s City of David may finally reveal the answer to one of archeology’s most enduring mysteries: the location of the Greek Acra citadel.
The exact spot of the famous stronghold that Antiochus IV used in the second century BCE to control Jerusalem and monitor activity on the Temple Mount has long been unknown due to a paucity of architectural remains that can be traced to the Greek presence in the capital.
Over the past hundred years of archeological research in Jerusalem, numerous theories have been put forth identifying the location of the Acra, which was eventually overtaken by the Hasmoneans.
‘“The new archeological finds indicate the establishment of a well-fortified stronghold that was constructed on the high bedrock cliff overlooking the steep slopes of the City of David hill,” the archeologists said in a joint statement.
A section of fortification was discovered under the Givati parking lot in the City of David south of the Old City walls and the Temple Mount. The fortification is believed to have been part of a system of defenses known as the Acra fortress, built by Antiochus as he sought to quell a Jewish priestly rebellion centered on the Temple.
Antiochus is remembered in the Jewish tradition as the villain of the Hanukkah holiday who sought to ban Jewish religious rites, sparking the Maccabean revolt.
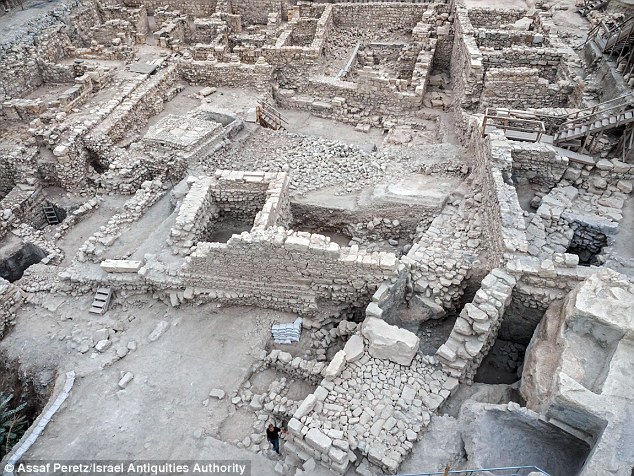

The remains of a massive wall (pictured) from a tower thought to have belonged to the ancient Acra fortress that dominated the City of David 2,000 years ago has been discovered under a car park in Jerusalem.
The Acra fortress was used by his Seleucids to oversee the Temple and maintain control over Jerusalem. The fortress was manned by Hellenized Jews, who many scholars believe were then engaged in a full-fledged civil war with traditionalist Jews represented by the Maccabees. Mercenaries paid by Antiochus rounded out the force.
The Book of Maccabees addresses the location of the Acra, stating: “And they built the City of David with a great and strong wall, and with strong towers, and made it a fortress for them: And they placed there a sinful nation, wicked men, and they fortified themselves therein.”
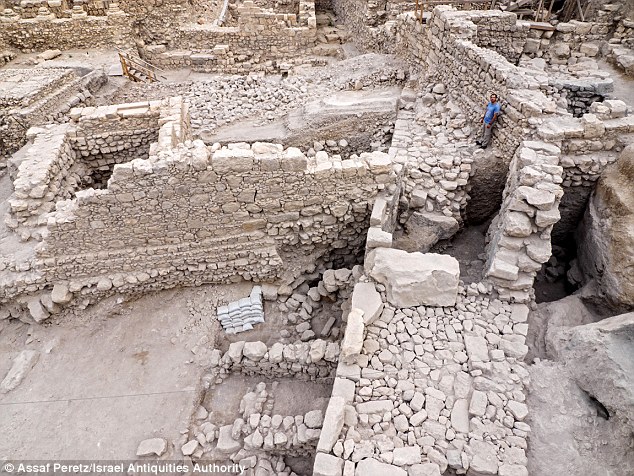

Archaeologists say the remains of the wall (pictured above) show the Acra had been in imposing structure.
In the first century CE, historian Josephus Flavius wrote of the Acra in Antiquities of the Jews: “…and when he had overthrown the city walls, he built a citadel in the lower part of the city, for the place was high, and overlooked the Temple; on which account he fortified it with high walls and towers, and put into it a garrison of Macedonians.”
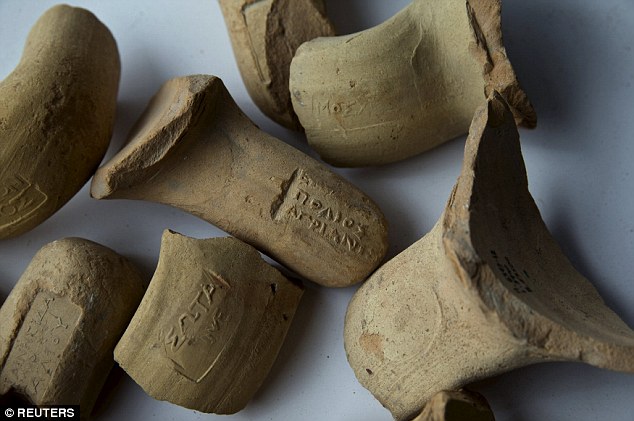

The remains of wine jugs and handles (pictured) were also discovered on the site of the ruins. They carry marks that indicate they were imported from the Aegean region of Greece.
At a Tuesday morning press conference outside the Old City walls at the City of David, where excavations have been conducted for more than a decade, researchers said they have finally exposed evidence of the Acra citadel on the City of David hill.
IAA excavation directors Dr. Doron Ben-Ami, Yana Tchekhanovets and Salome Cohen said the discovery affords an unprecedented opportunity to reconstruct the layout of the settlement in the city on the eve of the Maccabean uprising in 167 BCE.
“The new archeological finds indicate the establishment of a well-fortified stronghold that was constructed on the high bedrock cliff overlooking the steep slopes of the City of David hill,” the archeologists said in a joint statement.
The walls of the Acra were discovered on the ancient site of the City of David in east Jerusalem (illustrated).
The Hasmoneans regarded the Acra as a ‘thorn in the flesh’ of the city. It was eventually destroyed by Simon Maccabeus during the ensuing battles.
Dr Doron Ben-Ami, one of the excavation directors leading the dig on behalf of the Israel Antiquities Authority, said: ‘This sensational discovery allows us for the first time to reconstruct the layout of the settlement in the city, on the eve of the Maccabean uprising in 167 BCE.
“The new archeological finds indicate the establishment of a well-fortified stronghold that was constructed on the high bedrock cliff overlooking the steep slopes of the City of David hill,” the archeologists said in a joint statement.
“This stronghold controlled all means of approach to the Temple atop the Temple Mount, and cut the Temple off from the southern parts of the city.”
The researchers unearthed a section of a massive wall, which they said served as the base of a large watchtower that was four meters wide and 20 meters high. Additionally, a defensive sloping embankment composed of layers of soil, stone and plaster, designed to keep attackers away from the base of the wall, was located adjacent to the wall.
“This embankment extended as far down as the bottom of the Tyropoeon – the valley that bisected the city in antiquity, and constituted an additional obstacle in the citadel’s defenses,” the researchers said.
WHAT WAS THE ACRA?
- The Acra was an enormous fortress built on a hill in the middle of the City of David by Antiochus IV Epiphanes after he sacked the city in 168AD.
- A garrison of Macedonians were placed there to subdue the population of the surrounding city.
- It was described as an imposing fortress that withstood all attempts to conquer it.
- However, it finally fell following a long seige that starved the Greeks inside, forcing them to surrender.
- The Book of Maccabees locates the Acra within the City of David.
- It said: ‘And they built the city of David with a great and strong wall, and with strong towers, and made it a fortress [Greek: Acra] for them: And they placed there a sinful nation, wicked men, and they fortified themselves therein’
- – 1 Maccabees 1:35–38
- Another historical text, Antiquities of the Jews, also describes the city.It said: ‘…and when he had overthrown the city walls, he built a citadel [Greek: Acra] in the lower part of the city, for the place was high, and overlooked the temple; on which account he fortified it with high walls and towers, and put into it a garrison of Macedonians.’ – Flavius Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews 12:252–253
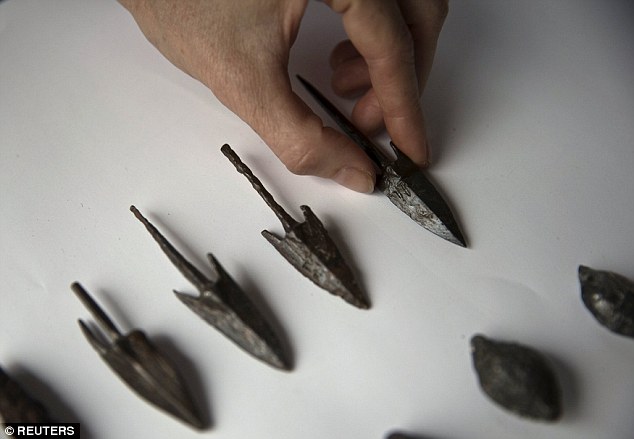

A series of bronze arrowheads (pictured) were discovered on the site. Archaeologists say they are the remains of battles fought between the Greeks garrisoned inside the fortress and the Maccabee rebels or sought to over throw them.
“Lead sling shots, bronze arrowheads and ballista stones that were discovered at the site and stamped with a trident, which symbolized the reign of Antiochus Epiphanes, are the silent remains of battles that were waged there at the time of the Hasmoneans in their attempt to conquer the citadel, which was regarded as a ‘thorn in the flesh’ of the city.”
According to historical sources, the stronghold was occupied by mercenaries, and Hellenized Jews documented great suffering that Jerusalem’s residents were exposed to at the hands of the Acra’s inhabitants.
“The fortification’s mighty defenses withstood all attempts to conquer it. It was only in 141 BCE, after a prolonged siege and the starvation of the Greek garrison in the Acra, that Simon Maccabeus was able to force its surrender,” the archeologists said.
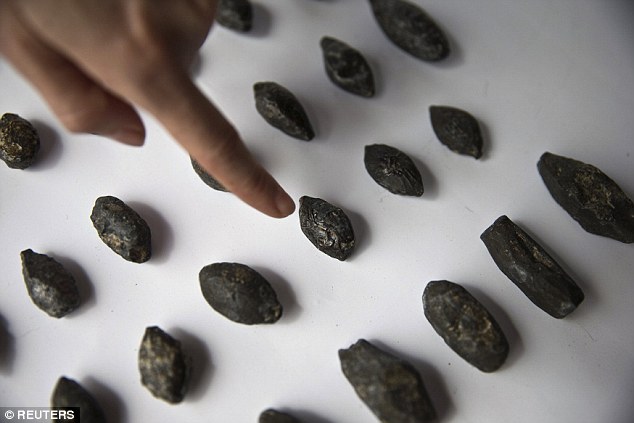

“The numerous coins, ranging in date from the reign of Antiochus IV to that of Antiochus VII, and the large number of wine jars that were imported from the Aegean region to Jerusalem, which were discovered at the site, provide evidence of the citadel’s chronology, as well as the non-Jewish identity of its inhabitants.”

‘The numerous coins ranging in date from the reign of Antiochus IV to that of Antiochus VII and the large number of wine jars that were imported from the Aegean region to Jerusalem, which were discovered at the site, provide evidence of the citadel’s chronology, as well as the non-Jewish identity of its inhabitants.’
The Elad Foundation, which operates the City of David National Park, is funding the extensive excavations, which have uncovered numerous artifacts from more than 10 different ancient cultures from Jerusalem’s history.
Emek Shaveh, a left-wing consortium of archeologists representing residents of the adjacent Silwan neighborhood, issued a statement after the discovery was announced to denounce an archeological facility slated to be built by Elad over the excavation site in the City of David’s Givati parking lot.

Lead sling stones and bronze arrowheads stamped with the symbol of the reign of Antiochus IV Epiphanes, evidence of the attempts to conquer the Acra citadel in Jerusalem’s City of David in Maccabean days. (Clara Amit/courtesy the Israel Antiquities Authority)
While Elad contends that the compound, named the Kedem Center, would be instrumental in drawing tourists by exhibiting ancient archeological findings, the European-funded NGO condemned the project as destructive.
Despite petitions to the High Court by Emek Shaveh and another NGO to block the Kedem Center, in June the National Planning and Building Appeals Committee approved the center, but ordered a scaleddown version.
Still, Emek Shaveh spokesman and archeologist Yonathan Mizrachi claimed that the historic discovery adds credence to the NGO’s argument that the center would somehow damage other archeological remains in the area.
“In light of this exciting discovery and all of the other unique archeological remains uncovered at the Givati site in Silwan/City of David, it is becoming absolutely clear that any construction on top of these antiquities should be avoided at all costs,” the statement said.
“We call on the Israel Antiquities Authority to fulfill its raison d’etre, and safeguard the remains by preventing development and construction at the site. It’s still not too late to retract the plan for the Kedem Compound, which, if built, will surely destroy this rare antiquities site.”
Following the committee’s ruling, Elad issued a statement lauding the decision as a victory for millions of tourists of multiple faiths.
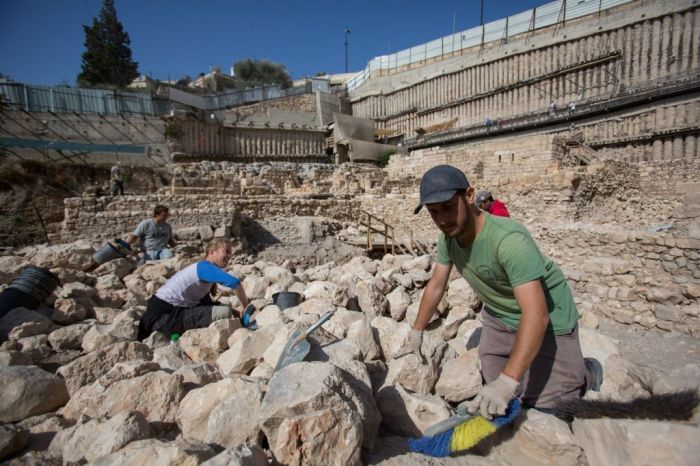

Archaeologists work near remains of the Acra citadel and tower in the City of David in Jerusalem. (Yonatan Sindel/ )
“The committee’s decision is a victory for the Kedem Center, with the committee acknowledging that it will benefit millions of people of all faiths and backgrounds who visit the City of David and its environs, seeking to connect with the history of ancient Jerusalem,” the statement read.
“Establishing a visitors center on this venue, without a doubt, will generate a high level of activity that complements the historic and archeological significance of the area.”
Source: JP
Join us at: He Is Coming -Are You Ready?
Jesus Christ was born, lived, died, and rose again for the sole purpose of saving us from our sins. Are you saved? The bible declares that “For whosoever shall call upon the name of the Lord shall be saved.” – Romans 10:13 (KJV). Salvation is turning your life over to Jesus Christ, believing that Jesus is the son of God, and renewing your mind with his spirit, that is done through repentance of sin, and following JESUS with all your heart, mind and soul. JESUS transforms lives, if you are ready for this life saving step, call upon your savior TODAY! Learn more here.
PROPHECY:
“…many shall run to and fro, and knowledge shall be increased” – Daniel 12:4 (KJV).
For thy servants take pleasure in her stones, and favour the dust thereof – Psalm 102:14 (KJV).




Reblogged this on Jewish and Christian News.
LikeLike